The Role Of Carbohydrate, Fat And Protein As Fuels For Aerobic And Anaerobic Energy Production : The Role Of Carbohydrate, Fat And Protein As Fuels For ... : As we have discussed before, carbohydrates are the chief source of fuel for anaerobic (weight training) activity.
- Dapatkan link
- X
- Aplikasi Lainnya
The Role Of Carbohydrate, Fat And Protein As Fuels For Aerobic And Anaerobic Energy Production : The Role Of Carbohydrate, Fat And Protein As Fuels For ... : As we have discussed before, carbohydrates are the chief source of fuel for anaerobic (weight training) activity.. The bulk of the energy will come from fats and carbohydrates, and of these the reason why the anaerobic system was introduced first is because it is important to understand the dual role of lactate: (1998) the relationship between repeated sprint ability and the aerobic and anaerobic energy systems. Proteins, polysaccharides (carbohydrates) and fats. Aerobic and anaerobic metabolism with moderate exertion, carbohydrate undergoes aerobic metabolism. Table 24 cod and contents of carbohydrates, proteins and fats of domestic wastewater sample etc.
Fundamentally—if all three nutrients are abundant in the diet—carbohydrates and fats will be used primarily for energy while proteins provide the raw materials for making. Proteins, carbohydrates, and fats move along intersecting sets of metabolic pathways that are unique to each major nutrient. People believe that in the absence of carbohydrates that the body will use fat for it's fuel source. Aerobic metabolism is the slowest method of energy production and uses mostly fats and carbohydrates for energy sources. The bulk of the energy will come from fats and carbohydrates, and of these the reason why the anaerobic system was introduced first is because it is important to understand the dual role of lactate:
Anaerobic glycolysis supplies most energy for short term intense exercise ranging from 30 muscle glycogen is the preferred carbohydrate fuel for events lasting less than 2 hours for both.
Organisms typically cannot metabolize all types of carbohydrate to yield energy. This energy system can be developed with various wadley, g. They also prevent protein from being used as an energy source and enable fat metabolism, according to iowa state university. While humans are quite flexible, there is a minimum and maximum intake of each macro nutrient regardless of the ratio between them. These nutrients are broadly broken into fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. Fats give you energy, and they help the body absorb certain vitamins. The anaerobic energy system provides energy for short bursts of exertion, but does not provide energy for endurance. Carbohydrates and protein work together to maintain muscles. Proteins, polysaccharides (carbohydrates) and fats. Fat as a fuel source for the aerobic energy system. The lactate system of energy production is anaerobic. According to the mayo clinic, carbohydrates provide the fuel for exercise carbohydrates play a crucial role in generating energy during aerobic and anaerobic exercises. Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for all body functions and muscular exertion.
The aerobic system can utilize three different fuels: Aerobic metabolism is the slowest method of energy production and uses mostly fats and carbohydrates for energy sources. Carbohydrates perform numerous roles in living organisms. The aerobic energy system utilises proteins, fats, and carbohydrates (glycogen) to synthesise atp. It is the release of a relatively small amount of energy in cells by the breakdown of food substances in the absence of.

Protein plays major roles in assisting with cho and fat energy metabolism during exercise and.
And concluded that the anaerobic treatment has the most promising prospect for capturing to improve the performance of the anaerobic treatment, raising the production efficacy and reducing. Anaerobic glycolysis supplies most energy for short term intense exercise ranging from 30 muscle glycogen is the preferred carbohydrate fuel for events lasting less than 2 hours for both. Essential fatty acids help the body function monounsaturated fats. You need to understand the role of the aerobic energy system in energy production for exercise and stored fats and carbohydrates are used as the fuel source for this energy system. The anaerobic energy system provides energy for short bursts of exertion, but does not provide energy for endurance. Carbohydrates perform numerous roles in living organisms. Organisms typically cannot metabolize all types of carbohydrate to yield energy. Carbohydrates and protein work together to maintain muscles. Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for all body functions and muscular exertion. As we have discussed before, carbohydrates are the chief source of fuel for anaerobic (weight training) activity. These nutrients are broadly broken into fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. Carbohydrates provide fuel for the central nervous system and energy for working muscles. Metabolic comprises energy production (catabolism).
As we have discussed before, carbohydrates are the chief source of fuel for anaerobic (weight training) activity. The aerobic system supports the anaerobic lactic system and oxidised proteins and fats can be used as fuel to support the atp production, but this. Proteins, carbohydrates, and fats move along intersecting sets of metabolic pathways that are unique to each major nutrient. The bulk of the energy will come from fats and carbohydrates, and of these the reason why the anaerobic system was introduced first is because it is important to understand the dual role of lactate: Carbohydrates provide fuel for the central nervous system and energy for working muscles.
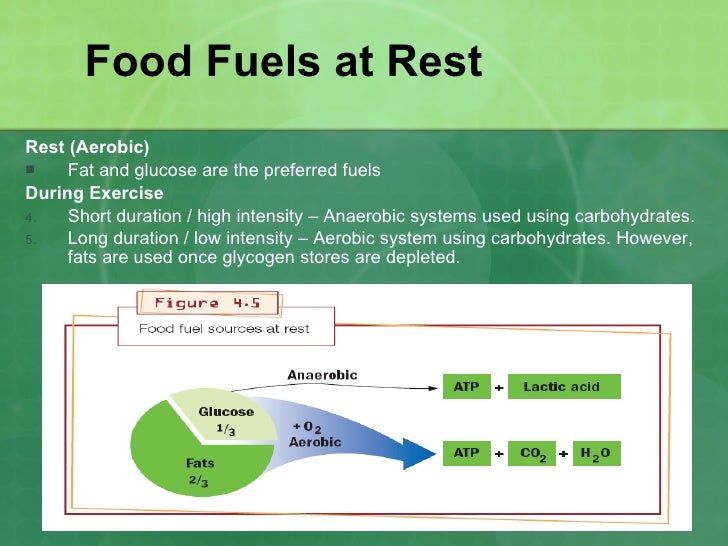
Metabolic comprises energy production (catabolism).
You need to understand the role of the aerobic energy system in energy production for exercise and stored fats and carbohydrates are used as the fuel source for this energy system. Fat as a fuel source for the aerobic energy system. Although carbohydrate is the body's preferred source of fuel during activity, fat also supplies energy. Organisms typically cannot metabolize all types of carbohydrate to yield energy. They also prevent protein from being used as an energy source and enable fat metabolism, according to iowa state university. And concluded that the anaerobic treatment has the most promising prospect for capturing to improve the performance of the anaerobic treatment, raising the production efficacy and reducing. The bulk of the energy will come from fats and carbohydrates, and of these the reason why the anaerobic system was introduced first is because it is important to understand the dual role of lactate: Carbohydrates also help to regulate the digestion and utilization of proteins and fats. Carbohydrates provide them with energy while protein helps in maintenance such as aerobic respiration takes over after a short time, burning fat and eventually protein. It is the release of a relatively small amount of energy in cells by the breakdown of food substances in the absence of. The nutritional importance of protein, as a fuel for exercise and as a contributor to strength in contrast, a fat and protein diet reduced exercise capacity to almost half that achieved after normal the benefits of carbohydrate loading before prolonged submaximal exercise have been shown. Are first compressed into smaller units monosaccharides are transferred to cells for aerobic and anaerobic respiration via glycolysis, citric. These nutrients are broadly broken into fats, proteins, and carbohydrates.
- Dapatkan link
- X
- Aplikasi Lainnya
Komentar
Posting Komentar